

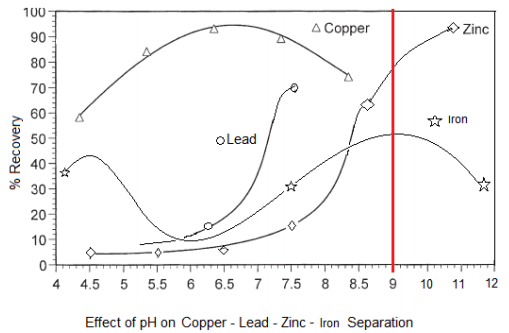
We assumed that P present in the sludge under neutral and alkaline conditions was in insoluble form bound up with magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca), because Ca and Mg also eluted from the sludge at low pH. The soluble concentrations of these elements changed dramatically with pH and were highest at pH 3. Sludge samples with neutral pH collected from three farms were incubated at pH values ranging from 3 to 10. ZAHN PRAX 2009: 12 84-86.With the goal of reducing the amounts of phosphorus (P), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn) discharged from swine wastewater activated sludge treatment facilities, we studied the elution of these elements from activated sludge at various pH values.
Zn element ph full#
^ Raab D: Fixation of full ceramic restorations – the advantages of cementation.^ Raab D: Befestigung von Zirkonoxidkeramiken.^ Raab D: Fixation of all ceramic restorations – the advantages of cementation.^ Raab D: Befestigung von Vollkeramiken aus Zirkonoxid."Zinc Phosphate Coatings on NonFerrous Substrates - Part I". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. "Comparison of the efficiency of inorganic nonmetal pigments with zinc powder in anticorrosion paints". Until the beginning of the First World War, he had a worldwide monopoly position with his cement. Otto Hoffmann invented this cement in 1892 and had it patented. Well-known dental brands in Germany and the world for zinc phosphate cement are Harvard cement and Hoffmann's cement. It is therefore used as liner to protect the pulp under composite fillings. Zinc phosphate cement has a high adhesive capacity to the tooth, metal, or even zirconium oxide.ĭespite its strong acidity, zinc phosphate cement does not damage the pulp (or the tooth nerve) during the setting phase. The excess produced during the cementation of dental restorations can be easily removed. Compared to other luting materials such as glass ionomer cement or composites, zinc phosphate cement is less sensitive to moisture.
Zinc phosphate cement has high compressive strength, low film thickness, minimal setting shrinkage and thermal expansion and is biocompatible. Zinc phosphate cement has only a low flexural strength and it does not stick to the dentin (it is a cement and not an adhesive). glass ionomer cement), but they have not displaced the classic phosphate cement, which continues to hold its own in the dental market with its simple and safe processing and good price-performance ratio. In recent years, newer adhesive cements on a different chemical basis have been added (e.g. It has the longest track record of use in dentistry. It is the standard cement to measure against. It is prepared by mixing zinc oxide and magnesium oxide powders with a liquid consisting principally of phosphoric acid, water, and buffers.
Zinc phosphate cement is used for cementation of inlays, crowns, bridges, and orthodontic appliances and occasionally as a temporary restoration. It is commonly used for luting permanent metal and zirconium dioxide restorations and as a base for dental restorations. Zinc phosphate cement is the classic dental cement par excellence. The anhydrous form has not yet been found naturally. Both are known from oxidation zones of Zn ore beds and were formed through oxidation of sphalerite by the presence of phosphate-rich solutions. A somewhat similar mineral is natural hydrous zinc phosphate called tarbuttite, Zn 2(PO 4)(OH). Natural forms of zinc phosphate include minerals hopeite and parahopeite. One common agent is sodium pyrophosphate. Zinc phosphate coats better on a crystalline structure than bare metal, so a seeding agent is often used as a pre-treatment. It has largely displaced toxic materials based on lead or chromium, and by 2006 it had become the most commonly used corrosion inhibitor. This white powder is widely used as a corrosion resistant coating on metal surfaces either as part of an electroplating process or applied as a primer pigment (see also red lead). Zinc phosphate is an inorganic compound with the formula Zn 3( PO 4) 2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
